CVD
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD)
Chemical vapor deposition (CVD) is a technique to coat substrates with thin films. The coating is hereby deposited out of the gas phase by chemical reactions.


Functional principle
Classical CVD
The substrate is heated while a gas is streaming over its surface. Due to the temperature a chemical reaction of the gas molecules takes place at the surface. With the time more and more molecules are adsorbed forming a coating.
CVD can be performed in various conditions (under atmospheric pressure, in vacuum etc.).
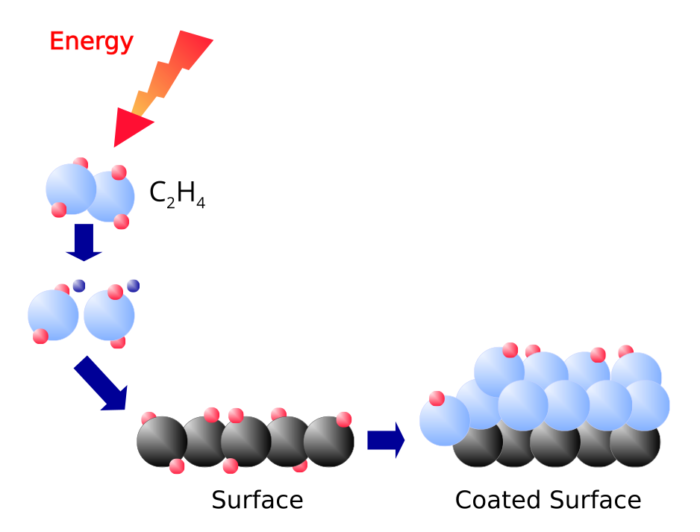
Plasma-enhanced CVD (PECVD)
Instead of temperature the reaction energy is supplied by plasma. A Plasma contains ions that can be accelerated electrically electricallyonto the substrate. The advantages compared to the classical CVD are:
- The process temperature is low enough to coat also temperature-sensitive plastics
- Higher deposition rates are possible
- The ions can be accelerated so strong that they form a hard coating. For example in a hydrocarbon plasma a diamond-like carbon (DLC) coating can be deposited.
- On plastics the coatings are chemically bound to the surface. They therefore show the optimal adhesion.
Plasma Electronic offers the following PECVD coatings:
- Diamond-like carbon (DLC)
- Different plasma polymers
- SiOx
- SiNx
We develop all PECVD processes according to your special needs. Contact us!